Create a campaign file¶
You define the initial disease outbreak and interventions used a campaign for a simulation through a JSON-formatted campaign file, typically called campaign.json. It is hierarchically organized into logical groups of parameters that can have arbitrary levels of nesting. For some interventions, there can be a very complex hierarchical structure, including recursion. The campaign file must be in the same directory as the configuration file and the name must be specified by the configuration parameter Campaign_Filename. This topic describes how to create the campaign file.
The EMOD Regression directory contains many different subdirectories that contain configuration, campaign, and other associated files to run simulations that represent real-world scenarios. Within the each subdirectory, there is usually a single campaign file (campaign.json), though some directories also include a campaign overlay file (campaign_overrides.json), which has been created by combining campaign_overrides.json with one of the default files in Regression/defaults. The naming of these files is an arbitrary convention used at IDM; you may name this files anything you choose. See Use campaign overlay files for more information flattening two campaign files.
For a complete list of campaign parameters that are available to use with this simulation type, see Campaign parameters. For more information about JSON, see EMOD parameter reference.
To distribute an intervention, you must configure the following:
- Campaign event
A JSON object that determines when and where an intervention is distributed during a campaign.
- Event coordinator
A JSON object that determines who will receive a particular intervention during a campaign.
- Intervention
A JSON object that determines what will be distributed to reduce the spread of a disease. An intervention can be distributed either to an individual (such as a vaccine, drug, or bednet) or to a node (such as a larvicide). Sometimes this can be an intermediate intervention that schedules another intervention.
The following is an example of campaign file that has two events (SimpleVaccine and Outbreak) that occur in all nodes at day 1 and day 30, respectively. Each event contains an event coordinator that describes who receives the intervention (everyone, with the vaccine repeated three times) and the configuration for the intervention itself.
Warning
The Outbreak must be the last event in the campaign file or none of the interventions will take place.
{
"Campaign_Name": "Vaccine",
"Use_Defaults": 1,
"Events":
[
{
"Event_Name": "SimpleVaccine",
"Event_Coordinator_Config": {
"Demographic_Coverage": 0.5,
"Intervention_Config": {
"Cost_To_Consumer": 10,
"Waning_Config": {
"class": "WaningEffectMapLinear",
"Initial_Effect" : 1.0,
"Expire_At_Durability_Map_End" : 0,
"Durability_Map" : {
"Times" : [ 0, 30, 60, 90, 120 ],
"Values" : [ 0.9, 0.3, 0.9, 0.6, 1.0 ]
}
},
"Vaccine_Take": 1,
"Vaccine_Type": "AcquisitionBlocking",
"class": "SimpleVaccine"
},
"Number_Repetitions": 3,
"Target_Demographic": "Everyone",
"Timesteps_Between_Repetitions": 7,
"class": "StandardInterventionDistributionEventCoordinator"
},
"Nodeset_Config": {
"class": "NodeSetAll"
},
"Start_Day": 1,
"class": "CampaignEvent",
},
{
"Event_Name": "Outbreak",
"Event_Coordinator_Config": {
"Demographic_Coverage": 0.001,
"Intervention_Config": {
"Antigen": 0,
"Genome": 0,
"Outbreak_Source": "PrevalenceIncrease",
"class": "OutbreakIndividual"
},
"Target_Demographic": "Everyone",
"class": "StandardInterventionDistributionEventCoordinator"
},
"Nodeset_Config": {
"class": "NodeSetAll"
},
"Start_Day": 30,
"class": "CampaignEvent"
}
]
}
Multiple interventions¶
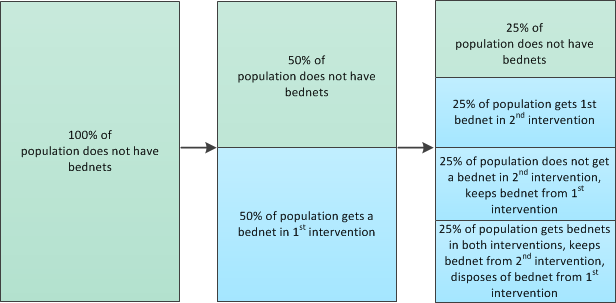
When creating multiple interventions, either of the same type or different types, they will generally be distributed independently without regard to whether a person has already received another intervention. For example, say you create two SimpleBednet interventions and both interventions have Demographic_Coverage set to 0.5 (50% demographic coverage). This value is the probability that each individual in the target population will receive the intervention. It does not guarantee that the exact fraction of the target population set by Demographic_Coverage receives the intervention.
By default, each individual in the simulation will have a 50% chance of receiving a bednet in both of the distributions and the two distributions will be independent. Therefore, each individual has a 75% chance of receiving at least one bednet.
Create a new campaign event¶
Although you can create campaign files entirely from scratch, it is often easier to start from an existing campaign file and modify it to meet your needs. Any of the campaign files in the Regression directory may be used. The simplest method is to edit the parameters or parameter values in the JSON file in any text editor. You may also create or modify the files using a scripting language, as with configuration files. See Create a configuration file for examples.
In the Events array, create a new empty JSON object. This object will contain all parameters for the new campaign event.
In this object, add and set values for the Event_Name and class parameters.
Add the Nodeset_Config parameter to define in which geographic nodes this even will occur.
Add the Event_Coordinator_Config parameter and assign a JSON object that will contain multiple parameters that control who receives the intervention.
In this object, add the Intervention_Config parameter and assign a JSON object that will contain multiple parameters that control which intervention is distributed.